Indian Railways overhauling its parcel business towards improved logistics efficiency
Posted: 2 December 2024 | Raman Arora | No comments yet
Raman Arora, from the Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS), Ministry of Railways, Govt. of India, shares his insight into Indian Railways’ new integrated cargo service that forms part of plans by the operator to overhaul its parcel business.


The logistics industry has a huge impact on the domestic and global economy of India and it is a critical enabler of India’s economic development. The industry in India is evolving rapidly due to the development of infrastructure and technology. The continuous growth of the industry presents a host of opportunities for logistics service providers, warehouse developers, technology providers, material and equipment suppliers and so on. According to the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index, India climbed six places to rank 38th out of 139 countries in 2023, demonstrating improvements in logistics efficiency and performance.
Policy measures such as the Gati Shakti Master Plan, National Logistics Policy, revision of Railways’ land use policy, and more recently the launch of 100 critical transport infrastructure projects for first and last-mile connectivity, will help in reducing the country’s logistics costs, improve multimodal connectivity and ramp up infrastructure.
India’s e-Commerce market is expected to reach US$111 billion by 2024, US$200 billion by 2026 and US$350 billion by 2030. Indian e-commerce is also expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27%.
Though the growth prospects of the logistics industry are very strong, the sector is also expected to contribute the highest amount of carbon emissions by 2050. Environmental concerns have drawn extensive attention around the globe and green logistics have become necessary for being sustainable.
Indian Railways (IR) have been a vital mode of transportation for goods and people for over a century, with a vast network spanning the length and breadth of the country. It is also considered as one of the green modes of transportation, with a significant savings of carbon emission compared to its peers. Modal share of railways in the national transport system is 28% as of the year 2023. IR’s freight segment transports around 1.6 billion tonnes of bulk cargo in a year (as in year 2023), yet the parcel segment is largely untapped, with major chunk of this market belonging to road and air.
The parcel is a money churner for many foreign railways, including in China. However, in India, rail is witnessing a consistent decline in revenue from parcel operations due to lack of investments and inefficient operations. The Rs 25,000 crore express industry, catering to top domestic and foreign e-tailers, is keen to see some changes in this system.
IR’s current strategy for moving general cargo is two-pronged – the parcels are moved either by passenger trains or by special heavy parcel van (VPH) trains. However, these approaches appear to have gone haywire as loading leased parcel vans and full parcel trains have dropped significantly due to high tariff, unreliable transit times, complex booking and delivery mechanisms, and self‑imposed environmental restrictions.
Challenges in parcel business
With rapid urbanisation, Indian Railways has not so far tapped a significant pie of their transport logistic market. IR’s parcel business contributes only around Rs 2100 Cr (~1%) of total earnings of more than Rs 2.25 lakh Cr.
Track sharing challenges involve the use of the same set of tracks for both passenger trains, parcel trains and freight trains with the former being prioritised, resulting in raised lead times for rail freight and parcel and its reliability.
Further, freight trains in India carry smaller loads and ply at lower speeds than global standards, again resulting in stretched out lead times and reducing the capacity of the network.
Moreover, lack of arrangement to aggregate smaller loads requires a shipper to contract a full train to move freight, as there is no standardised process to aggregate smaller loads for booking individual or partial wagons.
Opportunities
The Indian E-commerce industry has been on an upward growth trajectory and is expected to surpass the U.S. to become the second-largest E-commerce market in the world by 2034. Technology-enabled innovations like digital payments, hyper-local logistics, analytics-driven customer engagement and digital advertisements will likely support the growth in the sector.
With rail electrification progressing at a rate approximately nine times faster than a decade ago, from 1.42km per day in 2014-15 to about 19.6km per day in 2023-24, it shall also act as a catalyst for growth and sustainability in parcel business.
Projects of national importance, like Prime Minister’s Gati Shakti plan, is accrediting the major logistics players to innovate in this segment in order to close the ranks with China in logistics efficiency. That is critical for industrialisation and economic growth.
The modal share of Indian Railways in parcel business can be increased by creating an enabling framework for the movement of small cargo loads by facilitating the aggregation and by providing door-to-door services for MSMEs and small traders.
Thus, to keep pace with the industry trends and to meet the expectations of domestic and foreign e-tailers, IR plans to overhaul its parcel business through revolutionary measures. With a view to offer tailor made logistics to meet specific needs of customers and provide door-to-door services, the national transporter has recently introduced JPP-RCS (Joint Parcel Product- Rapid Cargo Service) Policy. This product essentially focuses on providing an integrated service, with first-mile and last-mile service for parcel being executed by aggregators and middle mile transportation being handled by the railways.
The policy enables the aggregators to register with Indian Railways for booking of space in JPP-RCS services with transit time assurance and reduced carbon footprints and introduces a state‑of-the-art technological solution for complete visibility and booking of these services.
The Centre for Railway Information Systems (CRIS), the IT arm of Indian Railways, has developed a Virtual Aggregation Platform (VAP) which will serve as an interface between aggregators and railways for JPP-RCS. The platform is an integrated product with seamless and secure data exchange between Freight Business Development (FBD) Portal, Parcel Management System (PMS) and Integrated Coach Management System (ICMS) of Indian Railways. The platform may also be integrated with the IT ecosystems of aggregators for seamless tracking of cargo by end customers.
Distinguished features of the Indian Railways Virtual Aggregation Platform
The Virtual Aggregation Platform is available as a hotlink on FBD Portal. One needs to sign up using a simple mobile number and e-mail ID based One-Time Password (OTP) verification process. Successful registration leads to a customised user dashboard with myriad information.
Available services
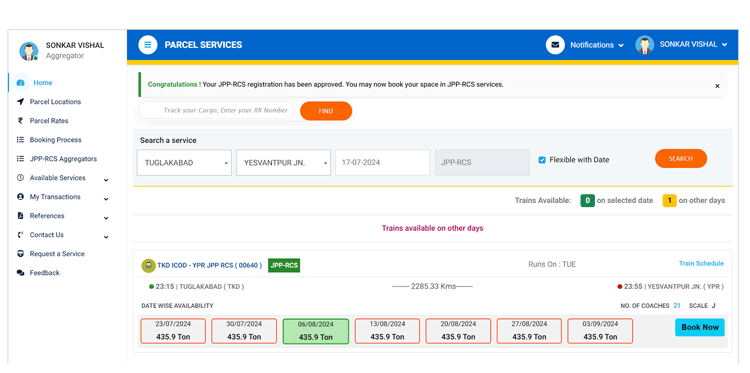
The user can view a complete list of all the JPP‑RCS trains available between a pair of stations. The list contains information of trains running on preferred date of booking and the trains which are available on alternative days. Date‑wise space availability, train schedule and coach composition with capacity of each parcel van (VPU) is also displayed for effective planning of cargo transportation.
An empanelled aggregator can book desired number of parcel vans (VPUs) in a JPP-RCS train for any chosen date through this option.
Booking of space
A simple-to-use interface facilitates booking of VPUs either in one-way or for round-trip transportation through a single transaction. The system adds an appropriate discount on round trip booking(s) as per the JPP-RCS policy. Payments for these bookings can be made online through any preferred mode, for example internet banking, NEFT/RTGS, UPI, credit card, debit card. Various insurance options are offered to the customer for securing the value of his consignment in case of any untoward incident.

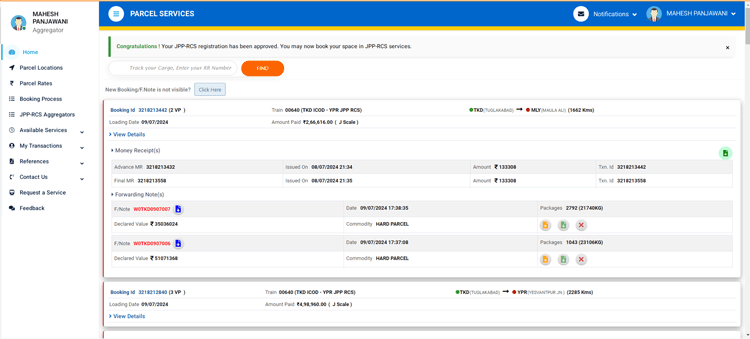
My transactions
Detail of all the bookings, forwarding notes, manifests, money receipts etc. are available through this option. The user may download these system-generated documents for onward submission to railways at the time of physical loading of consignment at the parcel terminals.
The system also awards Rail Green Point (RGP) Certificate, highlighting the contribution of the aggregator in saving carbon emissions for preferring rail over road for their cargo transportation needs.

Attempts have been made to ease out the usage of this application by providing access to a complete step-by-step user manual, an extensive set of frequently asked questions, policy document, contact detail of nodal officers and link to write any query/concern to the concerned railway authority.
Attention points, namely pendency of any activity (viz. F/Note generation, payment, manifest upload), information on various concession schemes and eligibility for bulk booking discount are immediately available as soon as an aggregator logs into this dashboard.
The platform also provides an easy to use, GIS based track and trace facility for real time tracking of the cargo.
Management Information System (MIS) reports
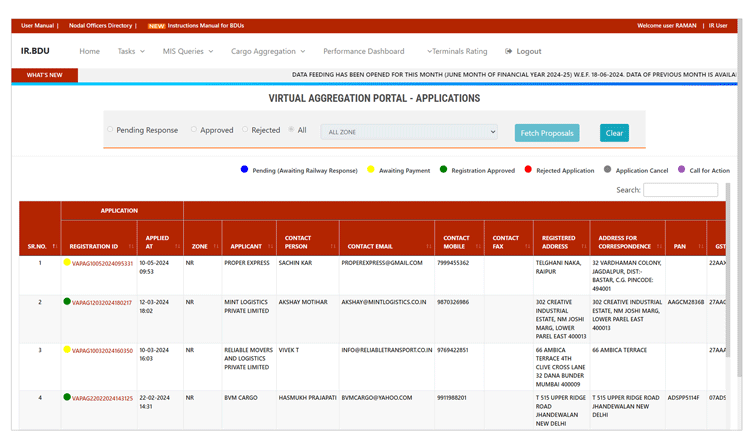
For IR Management, the platform also hosts an extensive set of MIS reports to analyse and monitor the business performance of the JPP-RCS model. The dashboard for Processing of Aggregators Applications, reports on date-wise and service‑wise bookings, pendency of payments, customer feedback and customers’ requests/intents for new source and destination pairs are available to railway authorities for planning and improving the customer satisfaction index. To facilitate deeper analysis, a number of filters and drill-down detail have been provided.

Virtual Aggregation Platform, as part of Freight Business Development Portal, is being actively used by aggregators as a single window, digital platform for booking, tracking and managing their cargo transportations in JPP-RCS services conveniently. Indian Railways through its new JPP-RCS policy does not only offer an economical transportation solution with transit assurance, but also offers a solution with significant environmental benefits. Virtual Aggregation Platform with its state-of-the‑art technological implementation adds to ease of doing business and transparency, for aggregators, MSMEs and small traders leading to a win-win situation for all the stakeholders. Thus, the platform is emerging as a big game changer for Indian Railways towards improved logistics efficiency.
Views presented in this article are the author’s own.


Issue
Related topics
Cargo, Freight & Heavy-Haul, Digitalisation, Freight, Indian Rail, Technology & Software