Delhi Metro’s environmental initiatives: A tale of innovation and dedication
Posted: 11 July 2024 | Anuj Dayal - Delhi Metro Rail Corporation | No comments yet
Anuj Dayal, Principal Executive Director of Corporate Communications at the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation, provides insight into the organisation’s unwavering commitment to sustainability through innovative eco-friendly practices and its significant achievements in reducing Delhi’s pollution and carbon footprint.


Concern for the environment and efforts to expand with sustainability have been central to the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation’s (DMRC) journey of nearly three decades so far. Since the commencement of construction work back in 1998, there has been a concerted effort to continuously innovate and implement initiatives that help in preserving the environment.
Delhi Metro was the first rail-based organisation in the world to claim carbon credits”
As a result, DMRC has had the privilege of being a pioneer in introducing a number of measures that have gone a long way in tackling the pollution crisis of Delhi and its peripheral areas. Delhi Metro was the first rail-based organisation in the world to claim carbon credits. DMRC is also a pioneer in the mass transit sector in solar power generation with a capacity of about 50MWp.
Now the Delhi Metro has added a new feather to its cap. The Delhi Metro’s Headquarters at Metro Bhawan has achieved carbon neutral certification, further solidifying its position as a leader in sustainable urban transportation. This milestone follows the earlier certification of DMRC’s staff quarters in Sector-50, Noida, as carbon neutral. It is a significant step in the organisation’s commitment to reducing its carbon footprint and combating climate change.
In line with the Government of India’s target to achieve net zero emissions by 2070, DMRC continues to work for carbon neutrality by adopting and implementing advanced environmental practices. The certification of Metro Bhawan as carbon neutral for the fiscal year 2023-24 under the Public Accountability Standard (PAS) 2060 is a testament to these efforts.
Eco-friendly measures at Metro Bhawan
DMRC has effectively reduced all greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions generated from Metro Bhawan through various innovative and eco-friendly initiatives. These include the installation of rainwater harvesting (RWH) pits, a sewage treatment plant (STP), the use of treated effluent for horticulture, water-efficient fixtures and an organic waste converter. These measures have significantly reduced the office’s environmental footprint.
In addition, Metro Bhawan has implemented numerous energy-efficient measures such as installing energy-efficient equipment, a rooftop solar photovoltaic (PV) plant and energy metering systems. These initiatives have drastically cut CO2 emissions from the building’s energy consumption. Metro Bhawan has also secured a Gold Rating from the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC). A target has been set to achieve a 5% reduction in overall energy consumption in the next year, aiming to further decrease the energy intensity of Metro Bhawan.


Credit: Delhi Metro Rail Corporation
Sustainable practices at construction sites
At its construction sites, Delhi Metro arranges for the planting of 10 trees for each tree cut”
At its construction sites, Delhi Metro arranges for the planting of 10 trees for each tree cut. All efforts are also made to transplant trees wherever feasible. In its premises, regular plantation drives are also conducted. All these efforts have helped significantly in enhancing the green cover of the city.
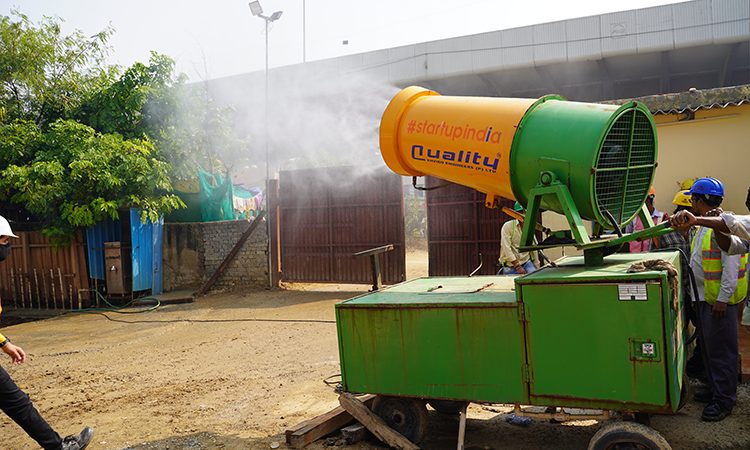
At the sites, elaborate dust and sound control measures are taken. Dust suppressants and mist-based spray systems are used to stop dust pollution. All vehicles leaving the construction sites must be mandatorily washed at the washing bays so that they do not litter the streets. All construction materials are adequately covered at the sites and the vehicles which carry such materials are also covered.
DMRC’s environmental engineers regularly visit the sites to ensure that these rules are stringently followed. DMRC is the first organisation in the country to take up such measures. These have gone a long way in the formulation of similar environment protection policies which are now being followed by other construction agencies as well.
At DMRC construction sites, construction and demolition (C&D) waste is segregated properly, stored and kept covered at a designated place. This stored waste is then transported to a recycling facility in covered trucks. To recycle the C&D waste, DMRC has set-up a C&D waste recycling facility of 150 TPD capacity at Ranikhera, Mundka, in an area of approximately three acres. About 95% of incoming C&D waste is recovered and recycled at this facility. The following products are recovered from recycling:
- Aggregates
- Sand
- Recovery of silt/soil
- RMC made with recovered material
- Value added products like kerb stones, pavement blocks and concrete bricks.


Credit: Delhi Metro Rail Corporation
Carbon credits and environmental impact
DMRC has also been certified by the UN for getting carbon credits for its modal shift project, which showed that a lot of passengers were preferring the Metro over their personal vehicles”
As mentioned earlier, Delhi Metro has contributed to environmental efforts by becoming the first railway project in the world to claim carbon credits for its regenerative braking and modal shift initiatives. DMRC has been certified by the United Nations (UN) as the first metro rail and rail based system in the world to get carbon credits for reducing GHG emissions. It has helped to reduce pollution levels in the city by 6.3 lakh tonnes every year, thus helping to reduce global warming.
Under the regenerative braking process for which DMRC earned carbon credits, whenever trains on the Metro network apply brakes, three phase traction motors installed on these trains act as generators to produce electrical energy which goes back into the overhead electricity (OHE) lines. The regenerated electrical energy that is supplied back to the OHE is used by other accelerating trains in the same service line, saving overall energy in the system as about 30% of electricity requirement is reduced.
The Delhi Metro Rail Corporation has also been certified by the UN for getting carbon credits for its modal shift project, which showed, through a scientific sampling technique, that a lot of passengers were preferring the Metro over their personal vehicles, resulting in a significant reduction in vehicular emissions in the National Capital Region (NCR) of India. It is difficult to provide documentary proof of the difference in energy consumption between two scenarios, i.e., ‘with Metro’ and ‘without Metro.’ However, DMRC proposed an innovative method of proving the emissions using scientific sampling techniques. After rigorous persuasion, the UN body finally agreed with this scientific and data driven technique.
Green building norms and solar energy initiatives
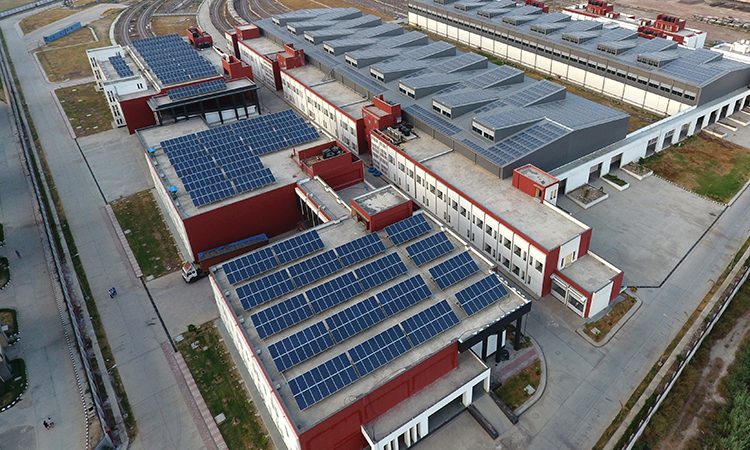
Since its third phase of expansion, DMRC has been designing all its buildings adhering to green building norms. After the completion of the buildings, they are rated as per a scientific rating mechanism, which the DMRC has jointly devised in association with the Indian Green Building Council (IGBC).
In fact, DMRC has now fully transitioned to a ‘Sustainable Built Environment’ and its approximately 14 million square feet of structures and facilities constructed as part of Phase 3 have been built to the highest ‘Green Standards’ with specific provisions for the conservation of energy as well as lower CO2 emissions, water saving, waste management arrangements, better indoor air quality and so on.


Credit: Delhi Metro Rail Corporation
DMRC has been a pioneer of solar energy usage for its requirements in the transport sector in the country. It is utilising the roof tops of its stations, depots, residential colonies and offices to set up solar power plants. While the first such plant was set up at the Dwarka Sector 21 Metro station with a capacity of 500 KWp, today, DMRC is producing 50 MWp of solar power from these plants established across the Delhi Metro network.
DMRC has unveiled an initiative called ‘CarbonLite Metro Travel’ to educate passengers about their contribution towards reducing carbon emissions by choosing metro trains instead of road-based motor vehicles”
DMRC is also using solar power for its traction requirements by drawing 345 million units (MUs) of electricity annually from the Rewa mega solar power plant in Madhya Pradesh. Through this unique arrangement, DMRC is drawing solar power from an off-site source located hundreds of kilometres away. This shows DMRC’s commitment to minimising the use of fossil fuel-based electricity sources for its operations.
Based on The Energy and Research Institute (TERI) survey, the latest figure for 2023 shows that around 5,97,361 vehicles have been taken off the road daily due to the Metro. Similarly, there have been reductions in the number of accidents and the release of pollutants into the air. These cumulative benefits have gone a long way towards improving the quality of air in the National Capital Region (NCR).
In another remarkable stride towards combating climate change and promoting sustainable transportation, DMRC has unveiled an initiative called ‘CarbonLite Metro Travel’ to educate passengers about their contribution towards reducing carbon emissions by choosing metro trains instead of road-based motor vehicles. Through this initiative, passengers are told of the average amount of CO2 emissions they save during their metro journeys in comparison to road-based motor vehicles. This enlightening statistic is prominently displayed on both paper and mobile QR tickets, ensuring widespread awareness of the positive impact of sustainable public transport. DMRC is possibly the world’s first metro service to introduce such a feature on its tickets.
Delhi Metro’s continuous efforts in environmental preservation have earned it a reputation as a frontrunner in sustainability within the global transportation landscape. In the days ahead, DMRC will continue to undertake such initiatives, as it recognises that the preservation of the environment is a solemn responsibility for every organisation.


Related topics
Electrification & Cabling, Passenger Experience/Satisfaction, Sustainability/Decarbonisation